Networking Glossary
Contents
Introduction
This page explains some of the fundamental concepts, components and terminology associated with standard computer networks. These networks are often referred to as local area networks (LAN). This type of network is technically known as an Ethernet network.
Cable
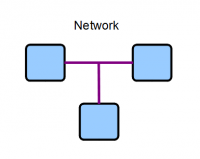
Network
An Ethernet network consists of two or more devices effectively connected together as shown in the diagram.
Addressing
IP Address
An IP address is a series of 4 numbers, in the range 0 to 255, assigned to each device on the network. Each device on the network needs a unique IP address to communicate with other devices. Problems will occur if two devices on the network have the same IP address.
Subnet Mask
A subnet mask is a series of 4 numbers, in the range 0 to 255, assigned to devices on the network. It is used as a filter, in conjunction with the IP address, to decide which other devices should be communicated with. Masks typically consist of a combination of the numbers 0 and 255. More advanced configurations may use other numbers but this is not common and will not be considered here.
more here...
Assignment
There are two ways to assign IP addresses and subnet masks to a device on the network, static assignmant and dynamic assignment.
Static Assignment (Manual)
Static (fixed) assignment is when the IP address and subnet mask are both manually programmed into the device. This is normally done using a setup menu on the device. Some devices do not support static assignment.
Dynamic Assignment (Automatic)
Dynamic assignment is when the IP address and subnet mask are both assigned automatically, over the network. This is done using a mechanism called DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). Devices that are setup for dynamic assignment send a DHCP request onto the network and then wait for a response containing the IP address and subnet mask they should use. A request is normally sent when the device is first connected to the network or immediately after it is power cycled.
DHCP Server
A DHCP server is a small configurable software component that responds to DHCP requests on the network. It keeps a record of the devices who sent requests. It ensures that every device is assigned a different IP address and the same subnet mask. It is important that only one DHCP server exists on the network. Problems will occur if more than one is present since devices would then receive multiple responses to their DHCP requests. Typically, DHCP server functionality is integrated into the router device on the network.
Dynamic Fixed Assignment
Dynamic fixed assignment (also known as Address Reservation) is a feature, supported by some DHCP servers, that allows devices to be dynamically assigned the same IP address every time. The advantage of this approach is that it harnesses the advantages of both static and dynamic assignment techniques.
MAC Address
Subnet
A subnet (subnetwork) is a subdivision of a larger network. Most networks are classed as subnets since they are typically connected to the internet and are thus a subdivision of that network. A subnet is defined by the range of IP addresses that are deemed valid on it's network.
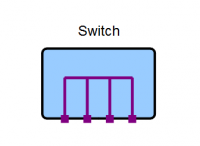
Network Switch
A network switch, often just referred to as a switch, allows multiple network devices to be connected together in a star formation. Switches come in different types and sizes. The most common type of switch is known as a "dumb" switch because it is not user configurable. A switch's size is defined by the number of network sockets, or ports, it has. The diagram below shows a four port switch.
A switch functions as a multipoint connector where any device, attached to any of the switch ports, is effectively connected to all other devices connected to any of the other ports.
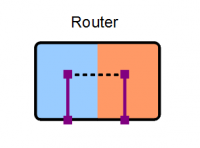
Router
A router is a device that manages the boundary between two networks or subnets.
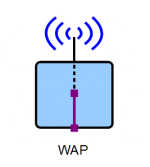
Wireless Access Point (WAP)
A WAP is device that provides wireless access to the network.
Modem
Power Over Ethernet (PoE)
Ethernet Over Power (Homeplugs)
Combination Boxes
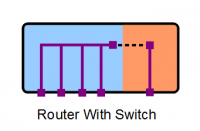
Router-Switch
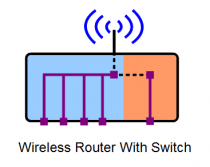
Router-Switch-WAP
Appendix
Advantages/Disadvantages Of IP Assignment Methods
Static IP Advantages
- The IP address is reliable as it always remains the same.
Static IP Disadvantages
- There is a small time/labour overhead in manual configuration
- There is a potential for error such as address conflicts
- If the device is moved to another network it will probably need a new address
- Need to keep a record of all addresses on the network