Networking Glossary
Contents
Introduction
This page explains some of the fundamental concepts, components and terminology associated with standard computer networks. These networks are often referred to as local area networks (LAN). This type of network is technically known as an Ethernet network.
Cable
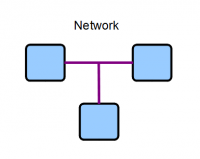
Network
An Ethernet network consists of two or more devices effectively connected together as shown in the diagram.
Since most devices only have one physical network connection socket, connecting more than two devices is not possible without the use of an additional device known as a network switch.
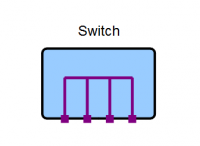
Network Switch
A network switch, often just referred to as a switch, allows multiple network devices to be connected together in a star formation. Switches come in different types and sizes. The most common type of switch is known as a "dumb" switch because it is not user configurable. A switch's size is defined by the number of network sockets, or ports, it has. The diagram below shows a four port switch.
A switch functions as a multipoint connector where any device, attached to any of the switch ports, is effectively connected to all other devices connected via any of the other ports.
IP Address
An IP address is a series of 4 numbers, in the range 0 to 255, assigned to each device on the network. Each device on the network needs a unique IP address to communicate with other devices. Problems will occur if two devices on the network have the same IP address.
Assignment
There are two ways to assign IP addresses to a device on the network, Static and Dynamic
Static Assignment (Manual)
Static (fixed) assignment is where a fixed IP address is manually programmed into the device. This is normally done using a settings menu on the device.
Advantages
Disdvantages
Dynamic Assignment (Automatic)
Dynamic Assignment is where the IP address is assigned automatically, by the network.
DHCP
Dynamic Fixed Assignment
Subnet
Subnet Mask
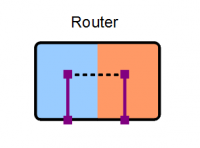
Router
A router is a device that manages the boundary between two subnets